In Zouxian County Power Plant, the steam turbine in the #8 unit is ultra-supercritical, once reheating, single-shaft, double back pressure, four-cylinder four-steam exhaust port condensing steam 1000MW steam turbine (model N1000-25.0/600/600). In overhaul of the unit, BCT101 system of BKC was installed.
Problems during unit start-up:
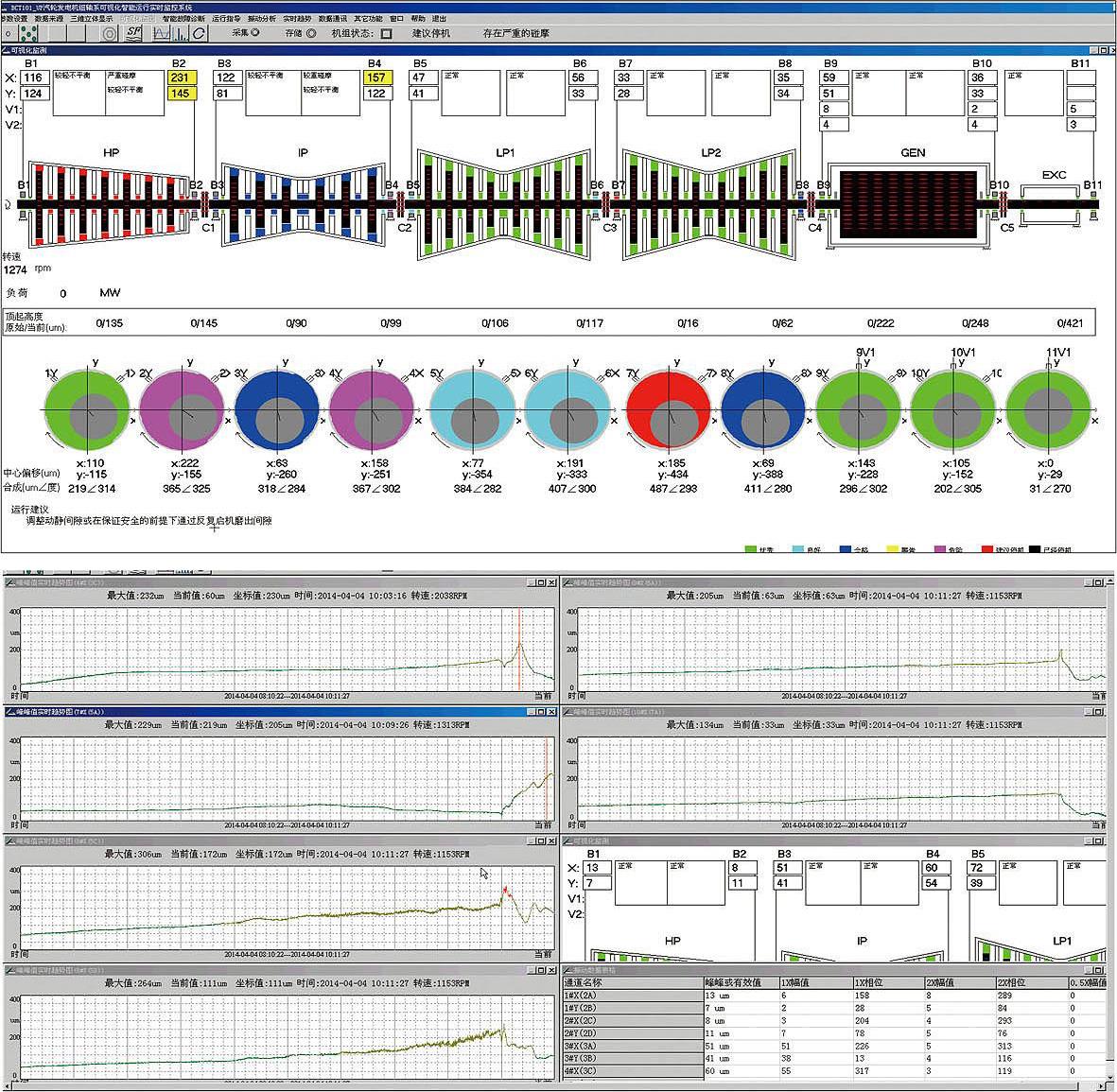
High and medium pressure rotor rubbing vibration
Phenomenon: after overhaul, after warm-up at 600rpm, the unit has small vibration, while in the plan of warm-up at 1500rpm, after the rotating speed reaches 1000rpm, #2 bearing has suddenly increased vibration amplitude and #1 &4 bearings see evident rise in vibration. When the machine is shut down, vibration continues to increase during speed reduction.
Analysis: based on the change of amplitude and phase, the mass imbalance of the high and medium pressure rotors can be ruled out. Increase in vibration is thus caused by static and static rubbing.
Result: after 4h manual rotating, the speed is increased to 1500rpm for warm-up, producing normal vibration.
Shaft rubbing vibration
Phenomenon: after #8 unit reached the constant speed, the amplitude of the shaft vibration of #8 and #9 bearings increased significantly, so did the amplitude of the low pressure cylinder and the medium pressure cylinder rotors.
Analysis: it can be seen (as shown in the figure below) that the amplitude changes while the phase changes significantly. When the critical speed is passed during shutdown, the vibration amplitude is significantly increased compared with the normal shutdown, indicating the thermal unbalance vibration caused by rubbing.
Result: after 4h manual rotating, the speed is increased to 3000rpm, producing normal vibration.
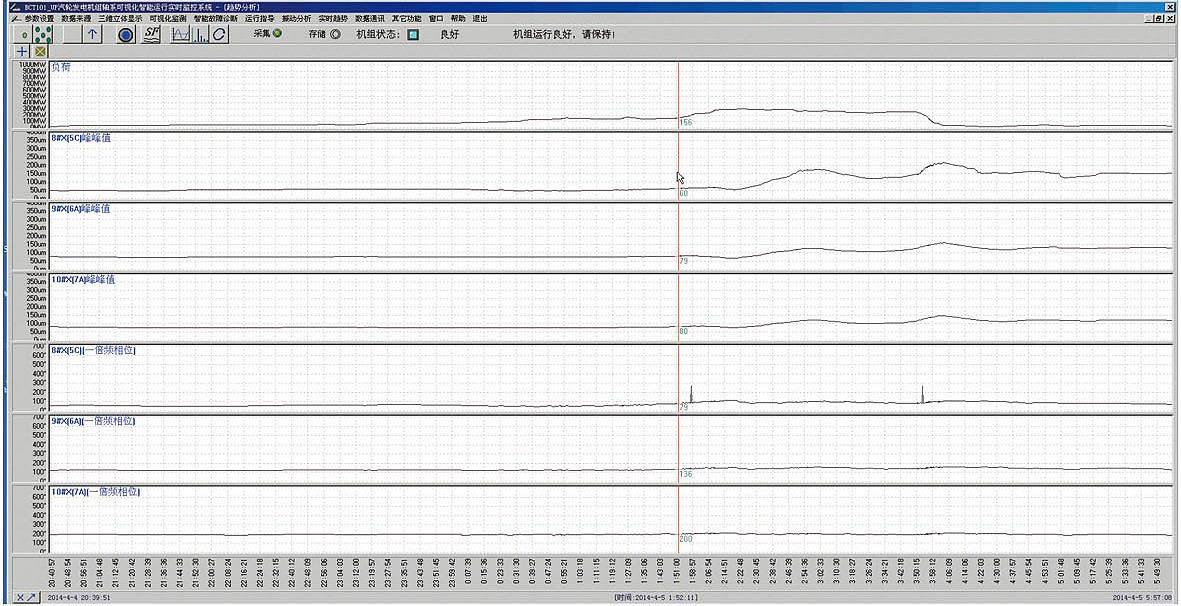
Low-pressure II rotor rubbing vibration with load
Phenomenon: after the #8 unit has a load of about 200MW, the vibration amplitude of the #8 bearing fluctuated significantly, so did the phase. Load was reduced after reaching 300MW, both the amplitude and phase were significantly changed (as shown below).
Analysis: since the vibration amplitude and phase change simultaneously, the analysis concludes vibration was caused by rubbing (if only the amplitude or phase maintains unchanged, it may be a thermal imbalance).
Result: the load was slowly increased and gradually to full load, with no abnormality of vibration happening.